
Latin America: End of “Supercycle” Threatens Reversal of Institutional Reforms
Latin America: End of “Supercycle” Threatens Reversal of Institutional Reforms https://redextractivas.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/NRGI_Logo_RGB_no_strapline-1024x582.jpg 1024 582 RLIE RLIE https://redextractivas.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/NRGI_Logo_RGB_no_strapline-1024x582.jpg- sin comentarios
Policies adopted in response to the end of the “supercycle” have slowed and, in some cases, reversed the reforms that moved the region toward greater decentralization, citizen participation, and environmental protection over the past decade. Latin American governments of the left and right used the commodities supercycle to drive growth and poverty reduction at an unprecedented pace. They also undertook institutional reforms aimed at improving governance at large.
Even before demand and prices for Latin American energy and minerals began to rise in the early 2000s, some Latin American countries launched processes of decentralization (Colombia and Bolivia); started to institutionalize mechanisms for citizens’ participation in decision making (Colombia and Bolivia); and built progressively stronger environmental management frameworks (Colombia and Ecuador). Peru pressed ahead with decentralization and participation at the start of the supercycle, and when it was in full swing, created a Ministry of the Environment.
Implementation of the reforms was subordinated by governments’ overarching goal of fostering investments in the extractive sector. Indigenous consultation rights in Peru, for example, were approved in the second half of 2011, but implementation was delayed a year and limited only to indigenous peoples in the Amazon Basin. President Ollanta Humala, giving in to the mining lobby, claimed there were no indigenous peoples in the Andes and that no consultations were needed around mining projects. Local pressure forced a reversal, and by early 2015 four consultation projects on mid-size mining projects were launched.
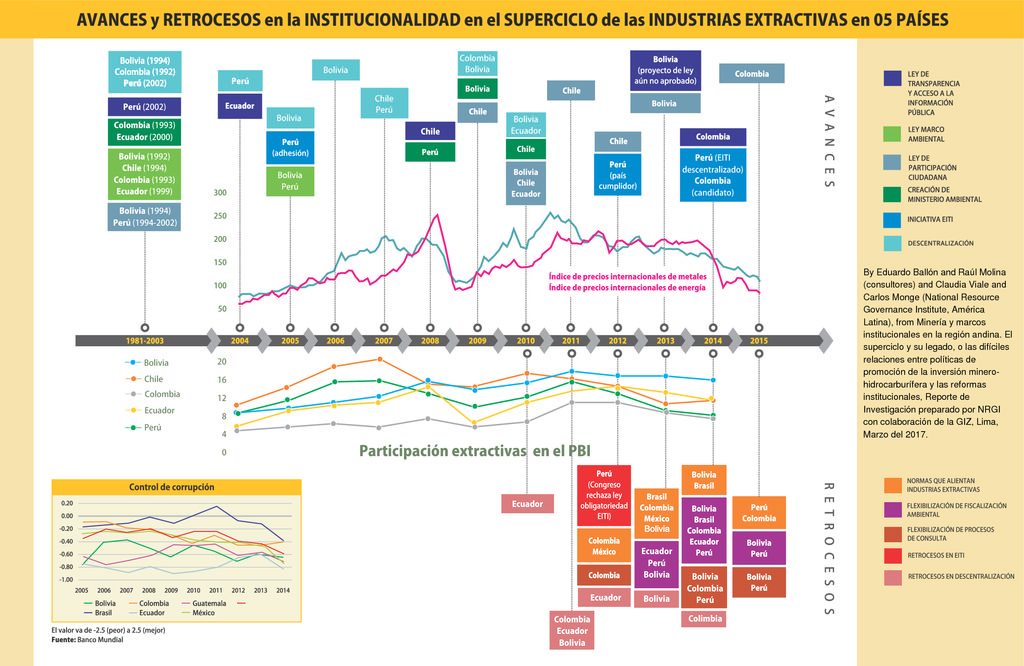 These reformist policies have suffered setbacks since the decrease in Asia’s and particularly China’s appetite for Latin American energy and minerals has caused prices to fall – and the value of exports, taxes, and royalties, and public incomes along with them. The latest ECLAC data show a decline in economic growth and a rebound of poverty both in absolute and relative figures. The gradual fall in the price of minerals starting in 2013 and the abrupt collapse in oil prices by the end of 2015 reversed this generally favorable trend.
These reformist policies have suffered setbacks since the decrease in Asia’s and particularly China’s appetite for Latin American energy and minerals has caused prices to fall – and the value of exports, taxes, and royalties, and public incomes along with them. The latest ECLAC data show a decline in economic growth and a rebound of poverty both in absolute and relative figures. The gradual fall in the price of minerals starting in 2013 and the abrupt collapse in oil prices by the end of 2015 reversed this generally favorable trend.
The response of the governments of resource-dependent countries has been “race to the bottom” policies, which included steps backward in fiscal, social, and environmental policies. Governments’ bigger concern has been to foster investments in the new and more adverse circumstances. In this new scenario, the processes of decentralization, participation, and environmental management have been negatively impacted as local authorities and citizens’ participation – as well as environmental standards and protocols – are perceived by companies and rent-seeking public officials as obstacles to investments.
Peru’s Law 30230 in 2014, for example, reduced income tax rates, weakened the oversight capacity of the Ministry of the Environment, and weakened indigenous peoples’ claim public lands.
The correlation between the supercycle years and the progress and regressions in reforms is clear. (click here for high-resolution graphic). During the supercycle – when huge amounts of money were to be made – companies and government were willing to incorporate the cost of citizen participation, decentralization and environmental standards and protocols. But now, governments are desperate for new investments to overcome the fall in economic growth and extractive rents, and extractive companies are not willing any more to assume these additional costs. Those who oppose the “race to the bottom strategy” are fighting hard to restore the reforms and to move ahead with decentralization, increased participation, and enhanced environmental management, to achieve a new democratic governance of the territories and the natural resources they contain.
April 7, 2017
* Carlos Monge is Latin America Director at the Natural Resource Governance Institute in Lima.
- Publicado En:
- Noticias
- Nuestra red